Groups of diseases that are transmitted to humans after contact with animals have a medical name “zoonosis“. There are about 850 zoonoses on the planet. Some people rarely encounter them, so there is a high probability that doctors have not discovered many more diseases.
Here are 10 human diseases that are initially transmitted to us from domestic or wild animals.
1. Toxoplasmosis
The simplest microorganism enters the human body after contact with a pet (cat, dog). The animal also picks up the pathogen from infected meat. The symptoms of the disease are usually erased, which makes it difficult to treat it promptly. The body forms tissue cysts that settle in healthy cells, striated muscles, and even the brain.
A pregnant woman can transmit the pathogen to the fetus, which may develop jaundice, thrombocytopenia, maculopapular rash, lymphadenopathy, hydrocephalus, deafness, convulsive syndrome, etc. after birth.
2. Q fever
One of the most contagious strains of bacteria, as theoretically the 1st colony will be enough to infect humans. The pathogen is transmitted by wild and domestic animals, as well as other people (mainly sexually). From an animal, the bacterium can be obtained as a result of contact with anybody’s fluids (milk, saliva, semen, excrement, etc.).
The first symptoms appear within 3 weeks: hyperthermia, headaches, sweating, fever, photophobia. In the absence of treatment with strong antibiotics, complications of the disease such as hepatitis and pneumonia are possible. Therapy usually takes from a few months to a couple of years, because to prevent relapse, it is necessary to kill every single bacteria.
3. Tularemia

The disease is characteristic of the continent of North America. It is caused by a bacterium that is transmitted from rabbits to humans through intermediate parasites (lice, ticks). Also, the pathogen enters the body after contact with the corpses of infected animals, through infected products and water from the drinking bowl.
The incubation period is about 3-5 days, after which symptoms develop: febrile fever, diarrhea, headaches, fever, arthritis, swelling of the lymph nodes and mucous membranes of the eyes, ulceration on the skin, and oral cavity, lethargy, etc. The acute course of the disease in the absence of adequate antibiotic therapy leads to the death of the patient. Most people die from dehydration, respiratory failure, which leads to pneumonia or suffocation.
4. MERS

This “young” disease was first diagnosed in Saudi Arabia 6 years ago. The carrier of the virus turned out to be a grave meshwing bat. The pathogen enters the human body not through direct contact with a sick bat, but through an intermediate carrier, which is most often domestic and industrial animals.
According to statistics from 4 years ago, outbreaks of the disease were diagnosed in 22 countries. However, almost all cases were linked directly or indirectly to Saudi Arabia.
5. Visceral leishmaniasis
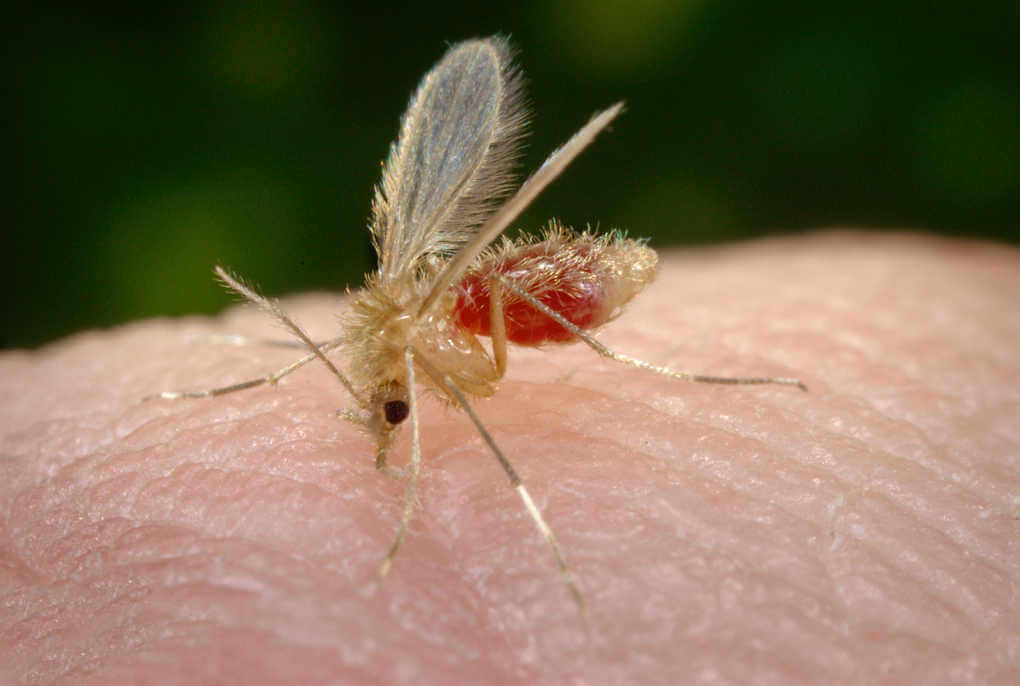
The disease is caused by a parasite that is transmitted through the bite of a female mosquito. Similar types of mosquitoes live in temperate regions of the planet and the tropics. Every year, up to 500 thousand people are infected with this form of leishmaniasis, while 50 thousand die. This human parasite is one of the most dangerous in history after sensational malaria.
In the absence of proper treatment, the mortality rate from the disease is one hundred percent. Symptoms resemble malaria: febrile temperature indicators, lethargy and weakness, anemia, enlargement, and changes in the structure of internal organs (spleen, liver).
Also, patients may darken the surface of the skin, there are characteristic ulcers. In its advanced form, the parasite attacks the immune system and weakens it, making it unstable to other dangerous diseases, such as pneumonia.
6. Toxocariasis
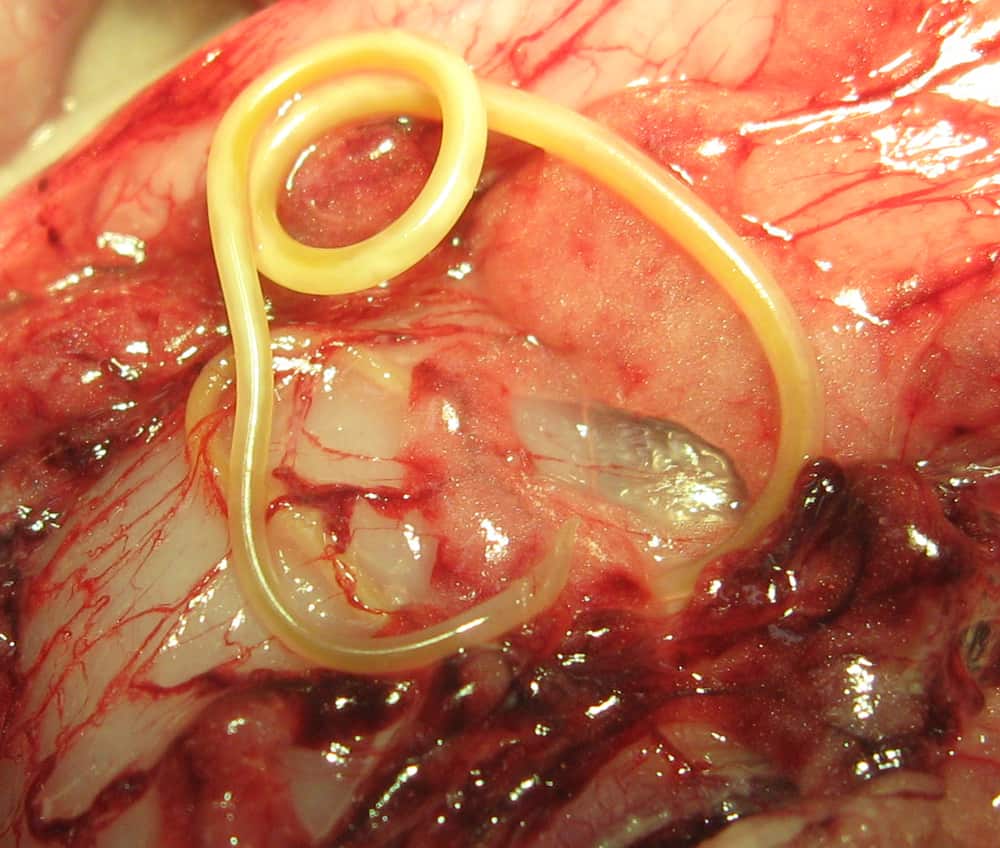
The disease is transmitted to humans through direct contact with the feces of infected wild (foxes) and domestic (dogs, cats) animals. Toxocariasis is a parasite that lays eggs in the host’s body. They can remain dormant for a couple of years, after which the larvae hatch and reach the gastrointestinal tract.
The patient notes symptoms characteristic of the disease: cough, colic and bloating, constant headache, hyperthermia. If toxocariasis has reached the eyes of the carrier, it may cause visual impairment and inflammation of the area, and in advanced cases, complete blindness occurs.
7. Trichinosis
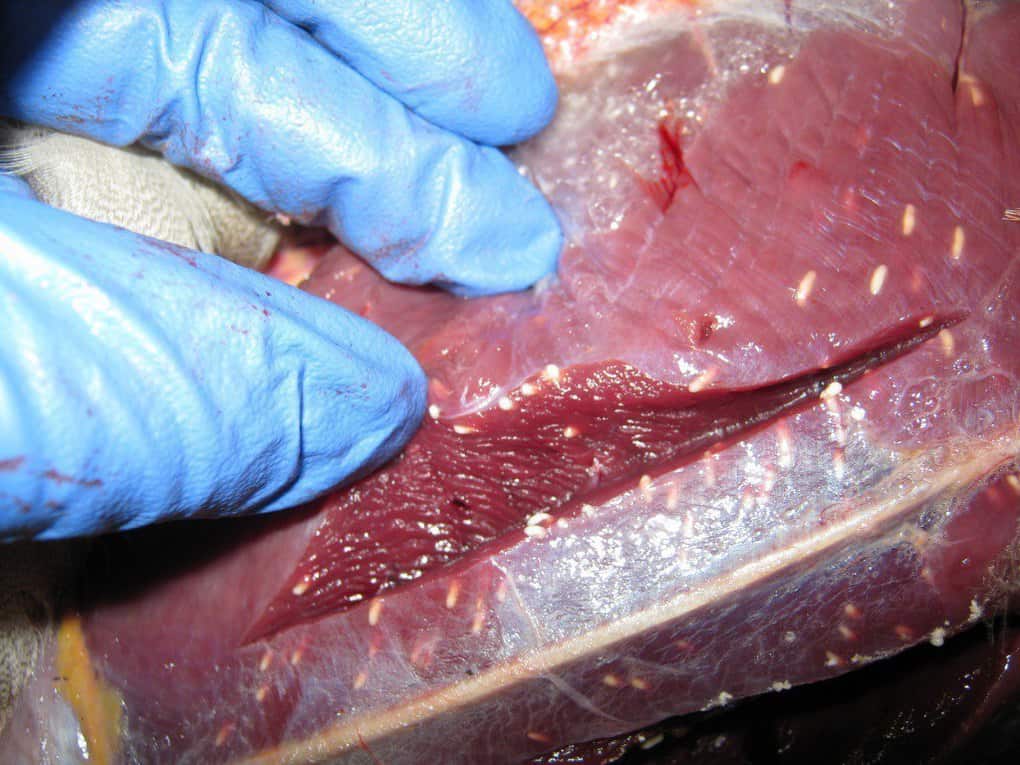
The causative agent of the disease is the larva of a round helminth. It enters the human body through the digestive system (eating trichinella meat). After 2-3 days, the larvae reach sexually mature forms and begin to actively multiply, clogging the lymphatic system with the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Larvae are also found in the bloodstream, muscle fiber. The disease is manifested by aching and sharp pain in the muscles, increased swelling of the face, persistent eosinophilia in blood tests.
8. Ornithosis

The virus is transmitted to humans from wild and domestic birds. Normally, at a heating temperature of about 70°C, it dies within 15 minutes, which makes it possible to accidentally eat a sick bird without consequences. But at low temperatures, the pathogen remains active for up to 60 days, and it is also resistant to drying. The disease affects about 100 species of birds, including geese, ducks, chickens, pheasants, parrots, and pigeons.
A person is infected mainly through the air and feed of a sick bird, as well as during post-slaughter processing (cutting, plucking, etc.). The disease manifests itself with symptoms of pneumonia: weakness and lethargy, difficulty breathing, congestion on the nasopharyngeal mucosa, loss of appetite, etc.
9. Cat scratch fever

As it turned out, harmless domestic purrs can inadvertently be carriers of a bacterium that provokes the disease. Through a bite or scratch, the pathogen enters the human body, causing swelling and redness of the affected area, swelling of the lymph nodes, and even the appearance of a rash after 1-2 (up to 8) weeks.
Often, the immune system independently copes with fever, which does not require medical treatment. But people with weakened immune systems (including children and elderly patients) need antibiotic therapy, otherwise, the disease may complicate to pneumonia and even coma.
10. Rabies

In the first place comes the disease with sad statistics of mortality. The rabies virus enters the human body through a bite or wound received from a sick animal. The highest concentration of the pathogen is found in saliva, and only then in the blood of a mammal. The incubation period of the disease is unpredictable, and sometimes it is completely asymptomatic.
Meanwhile, the virus enters the human brain, leading to a devastating and irreversible effect on the nervous system. With brain dysfunction, the control of the musculoskeletal system and respiratory system is disrupted, resulting in the death of a person.
Treatment under the Milwaukee protocol allows in 8% of cases to overcome the disease even at the time of the appearance of symptoms, although for this the patient is sent to an artificial coma and stuffed with significant doses of antiviral drugs.
Despite the rarity of such diseases, hundreds or even thousands of patients are admitted to clinics. Some of the zoonoses are easily treatable and involve the introduction of special serums, while others quickly lead to death. Be careful when coming into contact with domestic and wild animals.